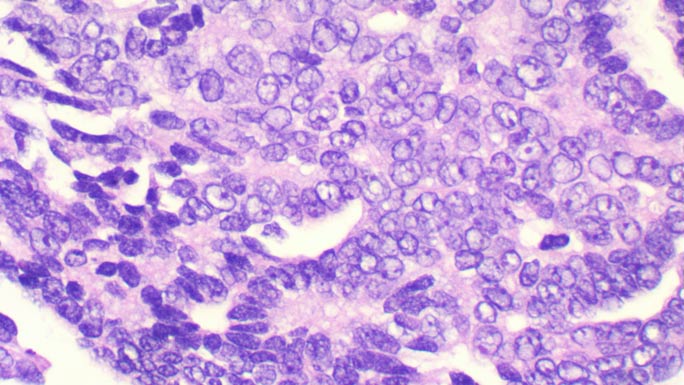
Low-Grade Epithelial Ovarian Cancer
Convenient Locations for Gynecologic Oncology Care
Request an Appointment
We are currently experiencing a high volume of inquiries, leading to delayed response times. For faster assistance, please call 1-855-702-8222 to schedule your appointment.
If you have symptoms of an urgent nature, please call your doctor or go to the emergency room immediately.
By submitting this form you acknowledge the risk of sending this information by email and agree not to hold the University of Chicago or University of Chicago Medical Center liable for any damages you may incur as a result of the transfer or use of this information. The use or transmittal of this form does not create a physician-contact relationship. More information regarding the confidentiality of this request can be found in our Privacy Policy.
* Indicates required field

Cancer Care Second Opinions
Request a second opinion from UChicago Medicine experts in cancer care.

Participate in a Clinical Trial
UChicago Medicine ovarian cancer experts are actively conducting clinical trials of new and promising treatments.

Gynecologic Cancer Prevention Clinic
Our cancer prevention experts provide comprehensive and personalized care for women at elevated risk for endometrial (uterine) cancer and ovarian cancer.